Satire criticizes or mocks societal norms/behaviors; Parody imitates the style of a particular genre, work, or author for comic effect.
Satire
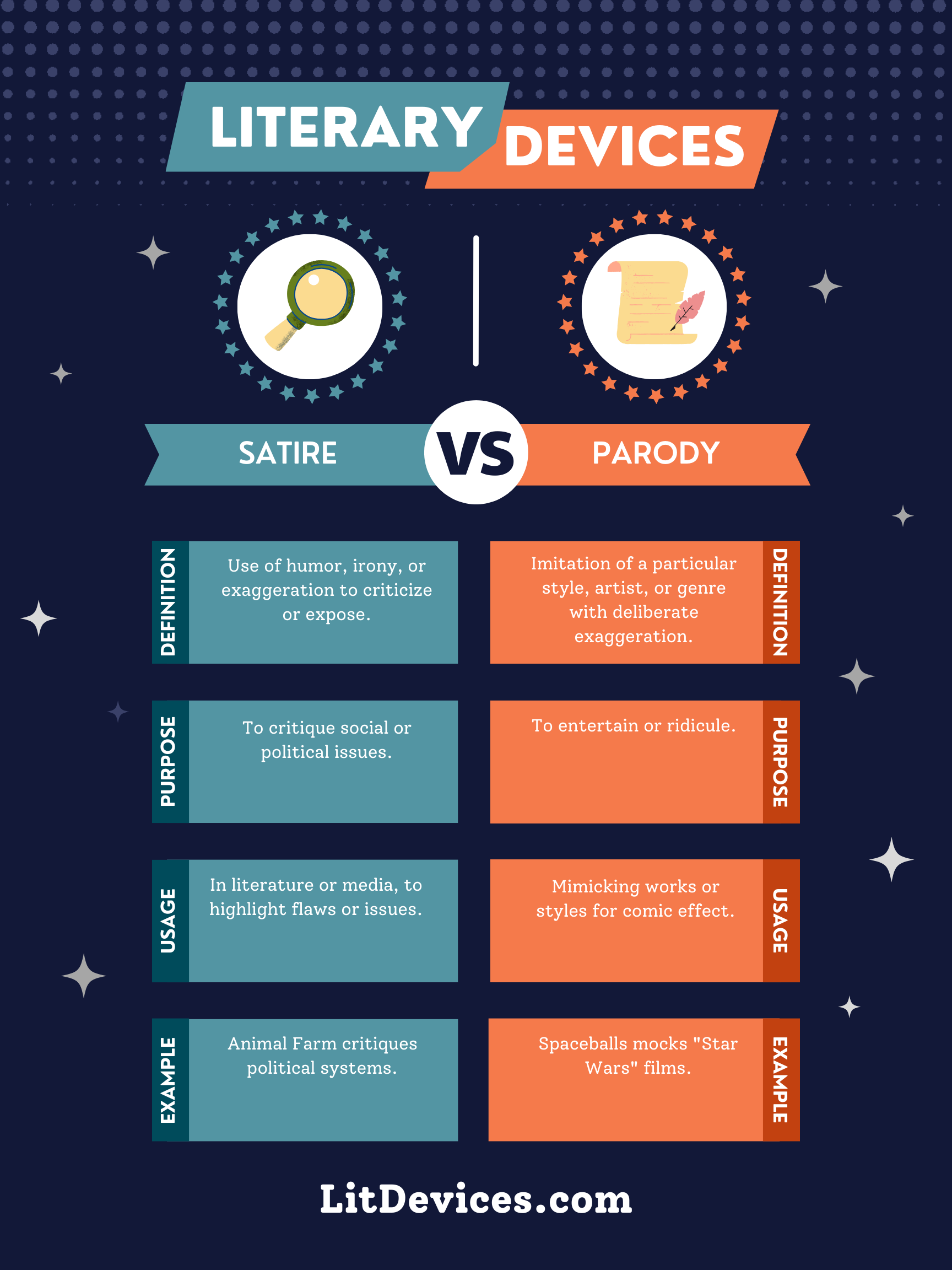
Satire is a genre of literature and performing arts that uses humor, irony, exaggeration, or ridicule to expose and criticize people’s stupidity or vices, particularly in the context of contemporary politics and other topical issues.
📚 Example: Jonathan Swift’s “A Modest Proposal” is a satirical essay that criticizes the British policy towards the Irish in the 18th century by absurdly suggesting that the Irish sell their children as food.
Parody
Parody is a form of satire that imitates the characteristic style of a particular writer, artist, genre, or work, often for comic effect and to draw attention to the original’s flaws.
🎭 Example: “The Simpsons” often parodies famous movies, TV shows, and even historical events, mimicking their style to create humor and critique the originals.
Summary
| Literary Device | Definition | Purpose | Usage | Relevant Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Satire | Uses humor, irony, exaggeration, or ridicule to expose and criticize societal norms or behaviors. | To highlight and critique flaws, stupidity, or vices in society, politics, and individuals. | Found in literature, essays, and media that aim to provoke thought and reform. | “A Modest Proposal” by Jonathan Swift. |
| Parody | Imitates the style of a specific genre, work, or author, often for comic effect. | To entertain and critique the original by highlighting its flaws or clichés. | Common in comedy, film, literature, and television that aims to mimic for humor. | “Spaceballs” parodies “Star Wars” series. |
Writing Tips
When crafting satire or parody:
- For Satire: Focus on the message you want to convey about the subject you are critiquing. Use wit, irony, and exaggeration as tools to highlight the absurdities and injustices of your target.
- For Parody: Develop a deep understanding of the original work or style you aim to parody. Emphasize its distinctive features and exaggerate them to create humor and draw attention to its faults or idiosyncrasies.
🖋 Example for Satire: Write a piece on contemporary social media culture, exaggerating the lengths to which people go for online attention to critique the superficiality and privacy invasions involved.
🖋 Example for Parody: Create a story that mimics the style of a famous detective novel but with overly convoluted plots and characters who are caricatures of traditional detective story archetypes, to poke fun at the genre’s tropes.
FAQs
Can parody exist without satire?
Yes, parody can simply mimic for humor without carrying the critical edge that satire often has. Not all parodies have a deeper message or critique.
Is satire always funny?
While satire often employs humor, its primary goal is critique and provocation rather than laughter. The humor in satire can be dark or even uncomfortable, aimed more at insight than entertainment.
How can I tell if something is satire or parody?
If it primarily aims to critique or expose societal flaws through humor, it’s likely satire. If it focuses on mimicking the style of something specific for comic effect, it’s parody.
Exercise
Identify whether the following scenarios are more indicative of satire or parody:
- A TV show that exaggerates the behaviors of reality TV stars to comment on the shallowness of celebrity culture.
- A novel written in the style of a classic detective story, where the detective is incredibly incompetent, highlighting the genre’s reliance on the detective’s brilliance.
- A short film that uses the exact style of old silent movies but introduces modern technology to create humor.
- An article that mimics the tone and structure of news reports to critique the sensationalism in media coverage.
Answers:
- Satire
- Parody
- Parody
- Satire
Interesting Literary Device Comparisons
- Irony vs. Sarcasm: Irony involves saying the opposite of what is meant to highlight a contrast, often subtly. Sarcasm is a form of verbal irony, used to mock or convey contempt, and is more direct and cutting.
- Allegory vs. Symbolism: Allegory is a narrative in which characters and events represent broader themes or concepts, offering a deeper moral or political meaning. Symbolism involves using symbols (objects, figures, or colors) to represent abstract ideas or concepts, adding depth and layers of meaning to the narrative.
- Metaphor vs. Simile: Both compare two different things to highlight similarities. Metaphors do so directly (“Life is a journey”), while similes use “like” or “as” to draw the comparison (“Life is like a journey”).