Personification gives human traits to non-human things; Anthropomorphism assigns human form to non-human entities.
Personification
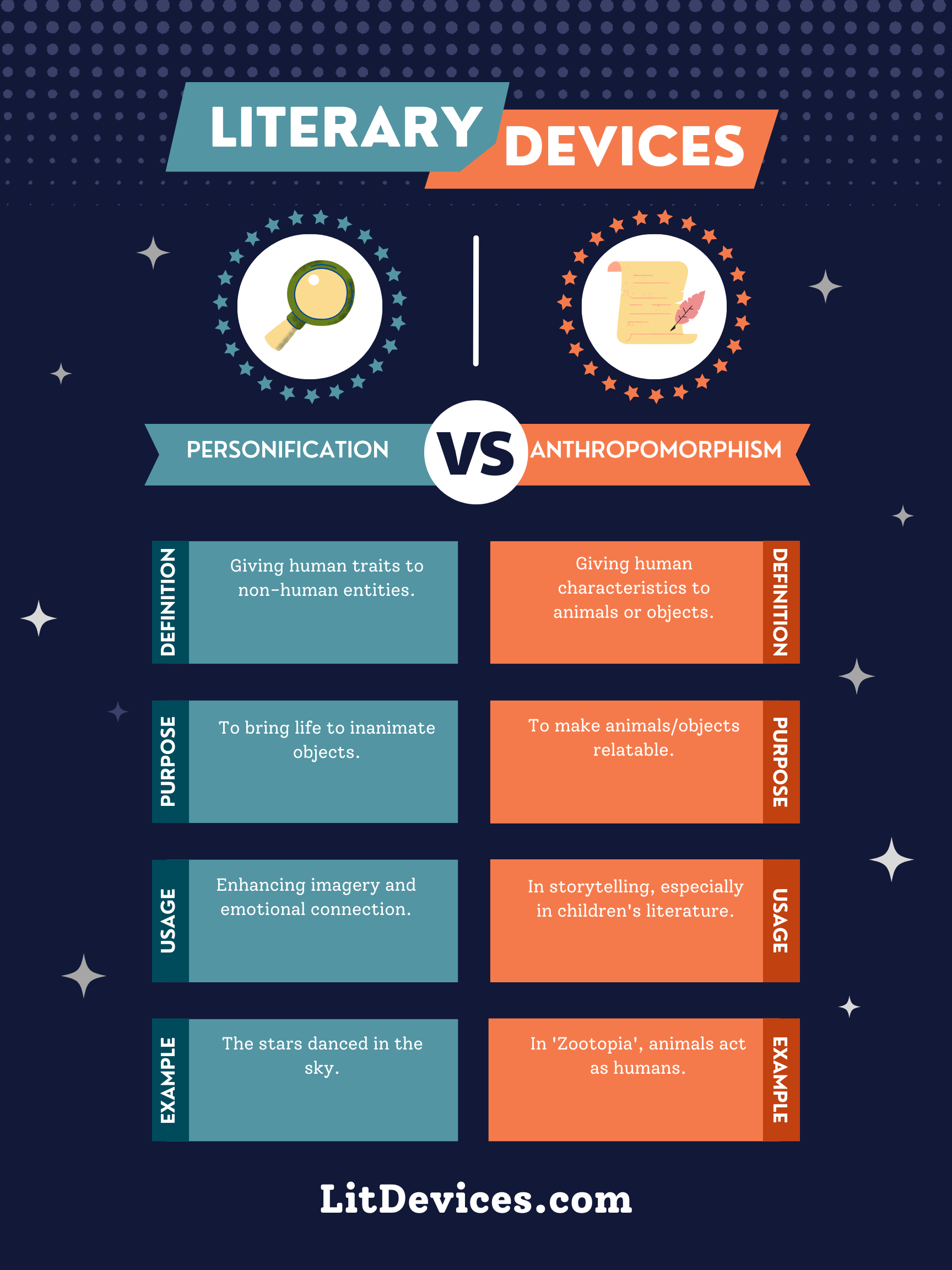
Personification is a literary device that attributes human qualities, emotions, or actions to non-human objects, animals, or abstract concepts, making them feel more relatable or vivid to the reader.
🌱 Example: “The wind whispered through the trees.” This suggests that the wind is ‘whispering’, a human action, to create a serene, secretive atmosphere.
Anthropomorphism
Anthropomorphism goes a step further by giving non-human entities—like animals or objects—not just human traits, but human forms, behaviors, and personalities, often allowing them to act as humans would.
🐻 Example: In the story of “Winnie the Pooh,” the bear Pooh and his friends are given human-like characteristics, such as talking, thinking, and feeling emotions just as humans do.
Summary
| Literary Device | Definition | Purpose | Usage | Relevant Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Personification | Attributing human qualities to non-human things or abstract ideas. | To create vivid imagery or convey feelings through inanimate objects or concepts. | Common in poetry and creative prose to enhance descriptive language. | “The stars danced playfully in the moonlit sky.” |
| Anthropomorphism | Assigning human form, behaviors, and characteristics to non-human entities. | To make non-human characters relatable and to explore human themes through them. | Used in fables, children’s literature, and animations. | “Mickey Mouse lives and interacts with others as a human would.” |
Writing Tips
When deciding between personification and anthropomorphism in your writing:
- Consider the purpose of your narrative. Use personification to enhance your descriptions and create atmosphere. Opt for anthropomorphism when you want non-human characters to drive the story or convey complex human emotions and themes.
- Keep your audience in mind. Anthropomorphism is particularly effective in children’s literature, as it can make concepts easier to understand and more engaging for young readers.
- Balance is key. Whether you’re giving a storm emotions or a rabbit human dilemmas, ensure the human traits you attribute are believable and serve the story’s overall tone and message.
📝 Example for Personification: “The city slept under the blanket of night.” It suggests the city is at rest, much like a human would be at night.
📝 Example for Anthropomorphism: Creating a character like Peter Rabbit, who wears clothes, talks, and experiences human-like adventures and challenges.
FAQs
What’s the key difference between personification and anthropomorphism?
Personification involves giving human traits to non-human objects or concepts, while anthropomorphism involves depicting non-human entities with human forms and characteristics.
Can personification and anthropomorphism be used together?
Yes, they can be used together, especially in works that aim to deeply explore themes or characters from unique perspectives.
Why use personification or anthropomorphism in writing?
Both devices can add depth to storytelling, making narratives more engaging and helping readers connect with non-human elements on a human level.
Exercise
Determine whether the following are examples of personification or anthropomorphism:
- The clock on the wall complained about being wound too tight.
- In “Zootopia,” Judy Hopps, a rabbit, serves as a police officer in a city of animals.
- The hurricane’s angry howl devastated the coastline.
- The Little Prince talks to a wise fox about life’s mysteries.
Answers:
Interesting Literary Device Comparisons
- Metaphor vs. Simile: Both compare two things, but similes use “like” or “as” while metaphors do not.
- Hyperbole vs. Understatement: Hyperboles exaggerate for effect, while understatements deliberately downplay the significance.
- Irony vs. Sarcasm: Irony involves stating something contrary to what is meant, subtly, while sarcasm is a form of verbal irony that is usually intended to mock or convey contempt.
Exploring different literary devices can enrich your writing, offering new ways to engage readers and convey your message.