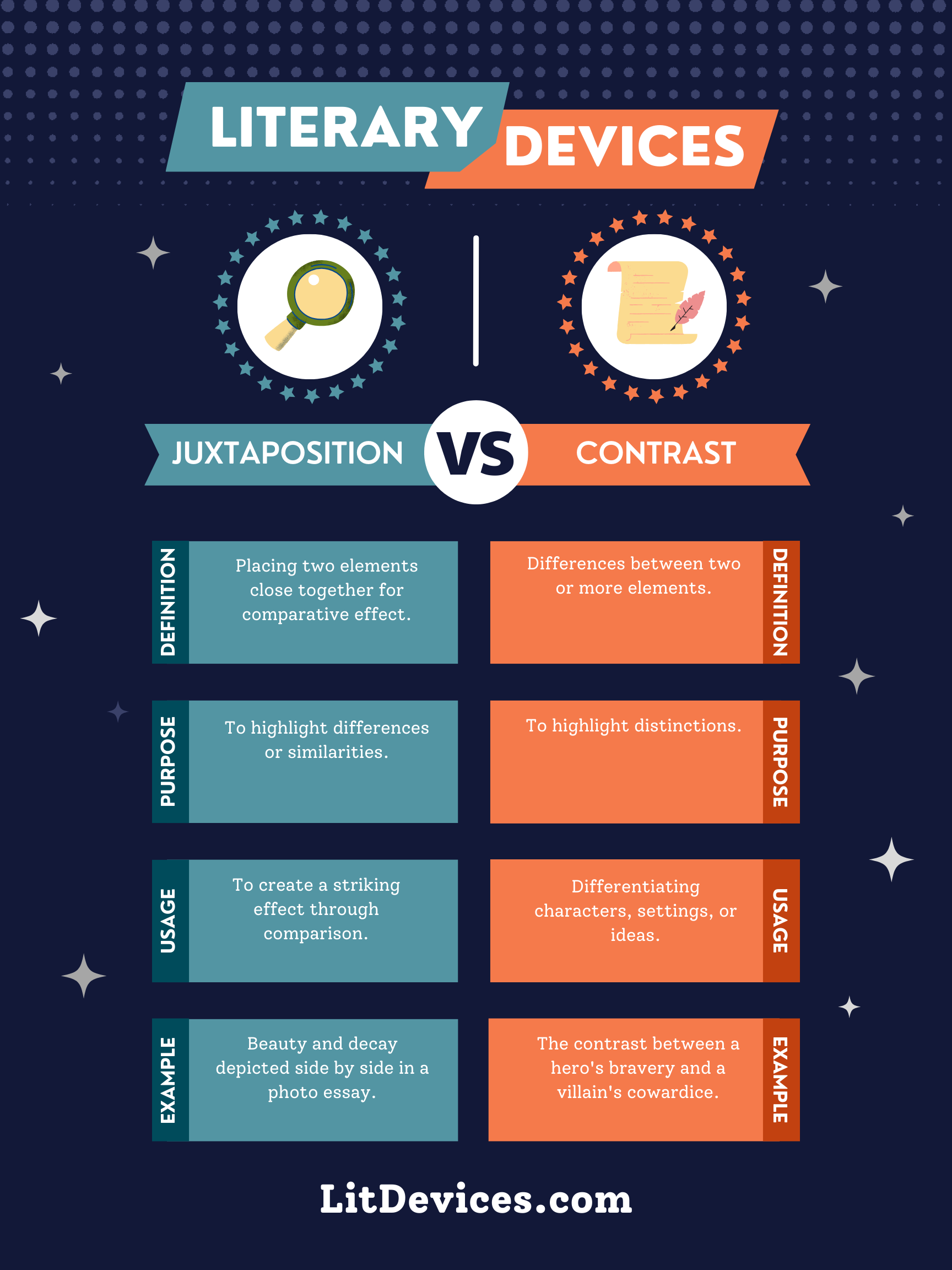
Juxtaposition places two elements close together for comparative effect; Contrast emphasizes the differences between two elements.
Juxtaposition 🖼️
Juxtaposition is a literary device that places two elements (characters, themes, concepts) side by side to highlight their differences or similarities in a subtle manner. For example, Charles Dickens’ “A Tale of Two Cities” begins with a juxtaposition of opposites: “It was the best of times, it was the worst of times…” This opening line sets up a comparison between the contrasting conditions of England and France during the French Revolution.
Contrast ⚖️
Contrast, on the other hand, directly emphasizes the differences between two elements. It’s more explicit than juxtaposition and is used to create tension or highlight distinctions. For instance, in Robert Frost’s poem “Fire and Ice,” Frost contrasts the fiery passion and cold indifference to explore the idea of the world’s end, showcasing the poem’s themes through stark differences.
Summary
| Literary Device | Definition | Purpose | Usage | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Juxtaposition | Placing two elements side by side to highlight their relationship. | To reveal subtle similarities or differences without direct comparison. | Used in scenes, themes, or characters to create depth or irony. | “A Tale of Two Cities” by Charles Dickens. |
| Contrast | Explicitly highlighting the differences between two elements. | To create tension, conflict, or emphasize distinctions. | Directly compares characters, settings, or themes to delineate clear differences. | “Fire and Ice” by Robert Frost. |
Writing Tips
For Juxtaposition Writers 📝
- Subtlety is Key: Use juxtaposition to show rather than tell. Place contrasting or similar elements side by side and let the reader draw their own conclusions.
- Theme and Character Development: Utilize juxtaposition to develop your themes or characters by placing them in contrasting scenarios or alongside contrasting characters.
For Contrast Writers 🔍
- Clarity in Differences: Make the distinctions clear and purposeful. Use contrast to highlight important thematic or character differences that drive the narrative forward.
- Tension and Conflict: Leverage contrast to create tension or to amplify conflicts within your story, making it more engaging for your readers.
FAQs
What is the main difference between juxtaposition and contrast?
Juxtaposition is about placing elements side by side to highlight their relationship subtly, while contrast explicitly points out their differences.
Can juxtaposition and contrast be used together?
Yes, they can complement each other in a narrative to enrich the storytelling by simultaneously highlighting similarities and differences.
How do juxtaposition and contrast affect a story’s mood?
Juxtaposition can create a nuanced mood or irony, whereas contrast can intensify the mood by delineating opposing forces or ideas.
Exercise
Task: Decide whether the following sentence uses juxtaposition or contrast: “In the heart of the bustling city, the tranquil garden remained a world apart, untouched by the chaos.”
Answer: Juxtaposition
Interesting Device Comparisons
- Metaphor vs. Simile: Both compare two different things, but metaphors do so by stating one thing is another, while similes use “like” or “as” for comparison.
- Foreshadowing vs. Flashback: Foreshadowing hints at future events in a story, building anticipation. Flashbacks, conversely, take the reader back to past events to provide background or context.
- Symbolism vs. Allegory: Symbolism uses symbols to represent ideas or concepts, while allegory uses characters and narrative elements to convey more complex messages or doctrines directly.