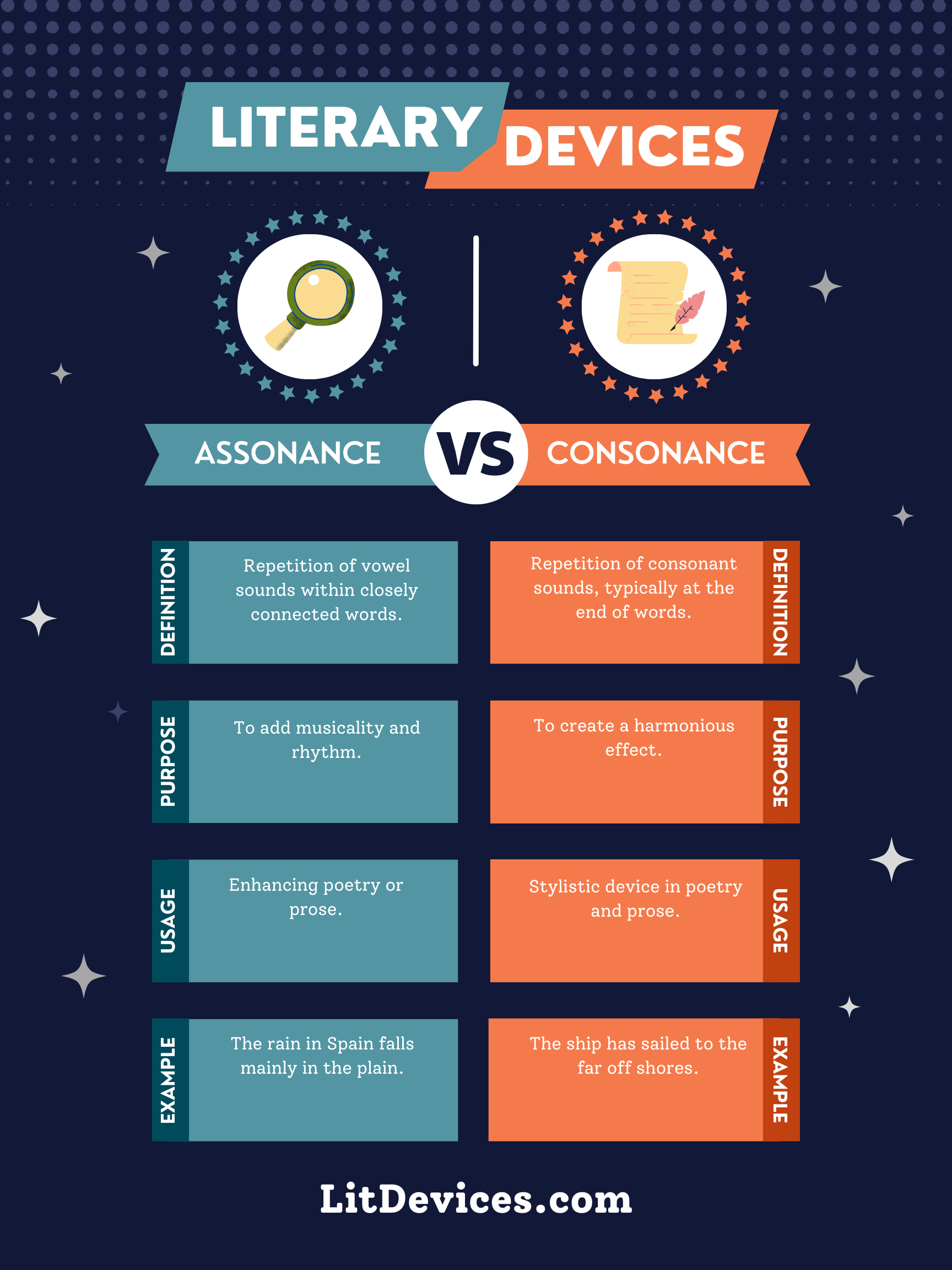
Assonance is the repetition of vowel sounds in nearby words; Consonance is the repetition of consonant sounds, typically at the end of words.
Assonance and consonance are both poetic devices that utilize sound repetition to create rhythm and mood in literary works. While they share similarities in their use of repetition, the specifics of their application and effect can vary greatly. Let’s explore these intriguing devices further. 🎶📝
Assonance
Assonance occurs when vowel sounds are repeated in close proximity within a sentence or line of poetry, creating an internal rhyming effect and adding musicality to the text. An example can be found in the phrase “The early bird catches the worm,” where the repetition of the “ea” sound in “early” and “ea” in “catches” creates a pleasing auditory effect.
Consonance
Consonance involves the repetition of consonant sounds, usually at the end of words, but also within words, contributing to the texture and flow of the language. A well-known example is the tongue twister “She sells seashells by the seashore,” where the “s” sound is repeated throughout the sentence.
Summary
| Literary Device | Definition | Purpose | Usage | Relevant Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Assonance | Repetition of vowel sounds in nearby words. | To add musicality and enhance mood. | Poetry, prose, songs. | “The early bird catches the worm.” |
| Consonance | Repetition of consonant sounds, typically at the end of words. | To provide texture and rhythm to language. | Poetry, prose, songs, tongue twisters. | “She sells seashells by the seashore.” |
Writing Tips
Incorporating assonance or consonance into your writing effectively can enhance its lyrical quality and emotive power. Here are some tips:
- Be Intentional: Use these devices to reinforce your theme or mood. Assonance can soften the tone, while consonance can make it more pronounced.
- Vary Your Use: Mixing assonance and consonance can add complexity and texture to your writing.
- Read Aloud: The true effect of these sound devices is best appreciated when heard. Read your work aloud to ensure the desired effect is achieved.
- Practice with Poetry: Experimenting with poetry can be a great way to refine your skill in using assonance and consonance, given its condensed and expressive nature.
FAQs
Can assonance and consonance appear in the same line or sentence?
Yes, both devices can be used together to create a rich auditory experience.
Are assonance and consonance only used in poetry?
While they are commonly found in poetry, both assonance and consonance can enhance prose and song lyrics as well.
How do assonance and consonance affect the reader’s experience?
These devices add rhythm, enhance mood, and can make passages more memorable due to their musical quality.
Exercise
Read the following sentence and identify the assonance and consonance:
“Quickly, the quiet squirrel jumps over the sleeping dog.”
Answers: Assonance is found in the repetition of the “ui” sound in “quickly” and “quiet.” Consonance is observed in the repetition of the “s” sound in “squirrel” and “sleeps.”
Other Interesting Literary Device Comparisons
- Metaphor vs. Simile: While both make comparisons, metaphors do so directly, whereas similes use “like” or “as” for comparison.
- Alliteration vs. Sibilance: Both involve repetition of sounds; alliteration is the repetition of consonant sounds at the beginning of words, whereas sibilance is the specific repetition of “s” and “sh” sounds.
- Personification vs. Anthropomorphism: Both attribute human characteristics to non-human entities, but anthropomorphism applies this to animals and objects, giving them human-like qualities and abilities.
Exploring the nuances of these devices can significantly enrich your writing and reading experiences, adding depth and vibrancy to the literary landscape. 📘🌟