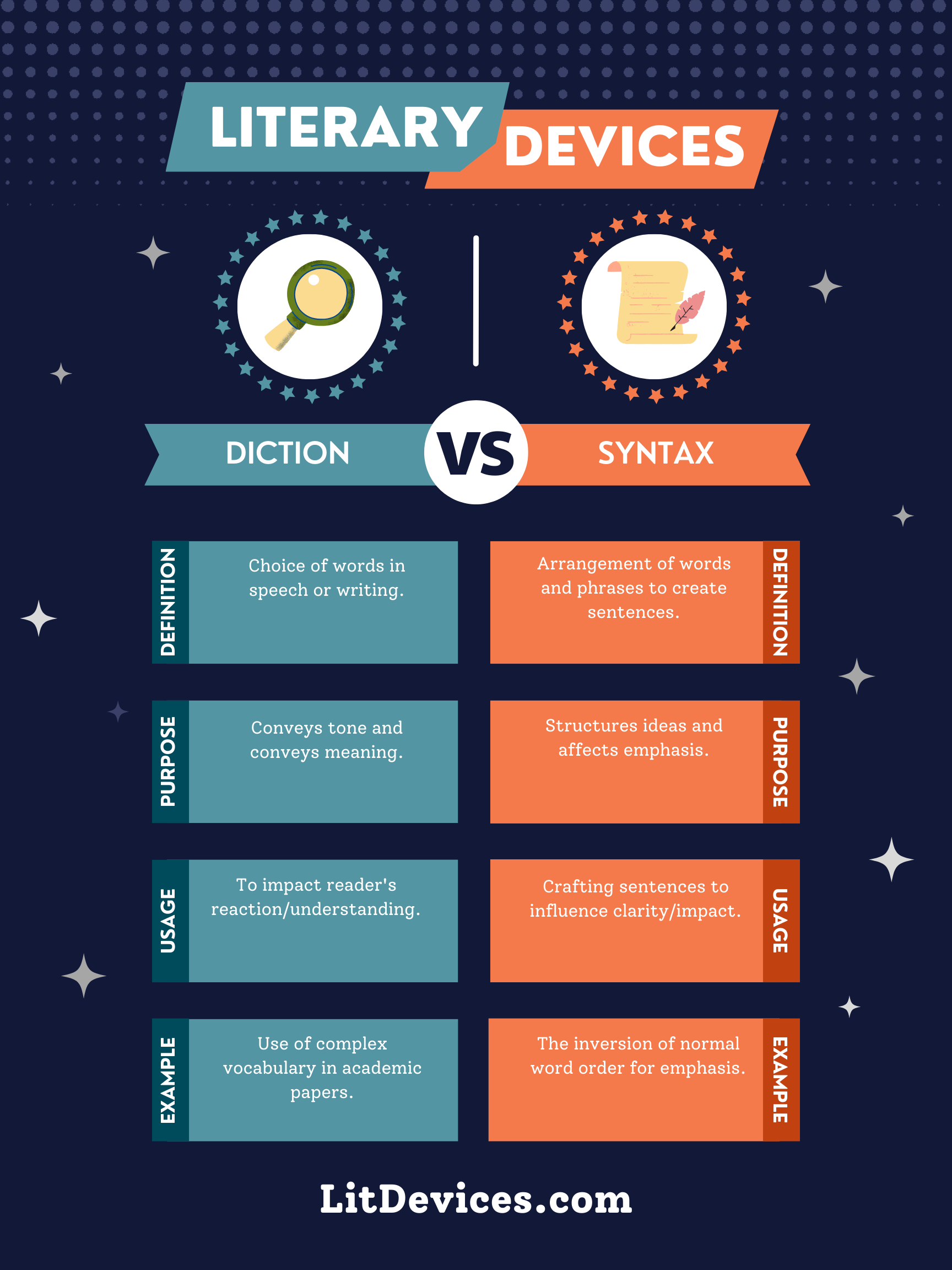
Diction refers to word choice and style of expression; Syntax is the arrangement of words and phrases to create well-formed sentences.
Diction
Diction is the selection of words and phrases by a writer or speaker. It reflects the style of expression and can greatly influence the tone, mood, and atmosphere of a piece of writing. Diction can be formal, informal, complex, simple, archaic, or jargon-filled, depending on the context and audience.
📖 Example: In “The Great Gatsby,” F. Scott Fitzgerald uses sophisticated and elegant diction to reflect the opulence and decadence of the Jazz Age.
Syntax
Syntax involves the arrangement of words and phrases to form coherent sentences. It encompasses sentence structure, length, punctuation, and the organization of words. Syntax plays a crucial role in conveying meaning, creating rhythm, and enhancing the readability of text.
📘 Example: In “To Kill a Mockingbird” by Harper Lee, the varied syntax reflects the complexity of themes and characters, using simple sentences to express clear truths and more complex structures for nuanced ideas.
Summary
| Literary Device | Definition | Purpose | Usage | Relevant Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diction | The choice and use of words and phrases in speech or writing. | To convey tone, mood, and atmosphere, affecting how the audience perceives the message. | Chosen based on the audience, context, and purpose of the writing. | Elegant diction in “The Great Gatsby.” |
| Syntax | The arrangement of words and phrases to create well-formed sentences. | To structure information coherently, affecting the pace and flow of the narrative. | Applied in constructing sentences to enhance readability and impact. | Varied syntax in “To Kill a Mockingbird.” |
Writing Tips
When honing your use of diction and syntax:
- For Diction: Be mindful of your audience and purpose. Choose words that accurately convey your intended message and tone. Experiment with specific nouns and vivid verbs to add clarity and depth to your descriptions.
- For Syntax: Play with sentence length and structure to influence the pace and rhythm of your writing. Use short sentences for impact and longer, complex sentences to build suspense or detail.
🖋 Example for Diction: To create a mysterious atmosphere, use precise, evocative words like “whispered,” “shadows,” and “lurking.”
🖋 Example for Syntax: To portray urgency or excitement, employ short, fragmented sentences. For reflective or complex ideas, use longer, compound-complex sentences.
FAQs
How do diction and syntax work together?
Diction and syntax complement each other; diction provides the building blocks (words), while syntax arranges these blocks into structures (sentences) to effectively convey meaning.
Can changing the syntax alter the meaning of a sentence?
Yes, rearranging words and phrases can significantly change the meaning or emphasis of a sentence, affecting how readers interpret the text.
Is diction more about the meaning of words while syntax is about the order?
Exactly. Diction focuses on the choice of words for their meaning and connotation, whereas syntax is concerned with how those words are organized and structured.
Exercise
Decide if the following descriptions are more related to diction or syntax:
- The author uses the word “galaxy” instead of “space” to emphasize the vastness and beauty.
- A sentence is structured in passive voice to highlight the action rather than the subject.
- A paragraph starts with short, choppy sentences to mimic the protagonist’s panic.
- The use of slang and colloquial language to make dialogue more realistic.
Answers:
Interesting Literary Device Comparisons
- Metaphor vs. Simile: Both are comparative devices used to enhance descriptions; metaphors imply direct comparison without using “like” or “as,” whereas similes make comparisons explicit.
- Foreshadowing vs. Flashback: Foreshadowing hints at future events, creating anticipation or suspense, while flashback provides a backward glance at events to add context or depth to the story.
- Alliteration vs. Assonance: Alliteration repeats consonant sounds at the beginning of words close together, while assonance repeats vowel sounds within words, contributing to the musicality and rhythm of the